Tapered Roller Bearing vs Spherical Roller Bearing
Roller bearings are indispensable in modern industrial machinery, playing a pivotal role in various applications. This article aims to elucidate the differences between two critical types of roller bearings: tapered and spherical. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions in industrial applications.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are a specific type of bearing designed with tapered rollers arranged between inner and outer ring raceways. They converge at a common point on the bearing axis, ensuring optimal rolling conditions and efficient distribution of loads across the roller.
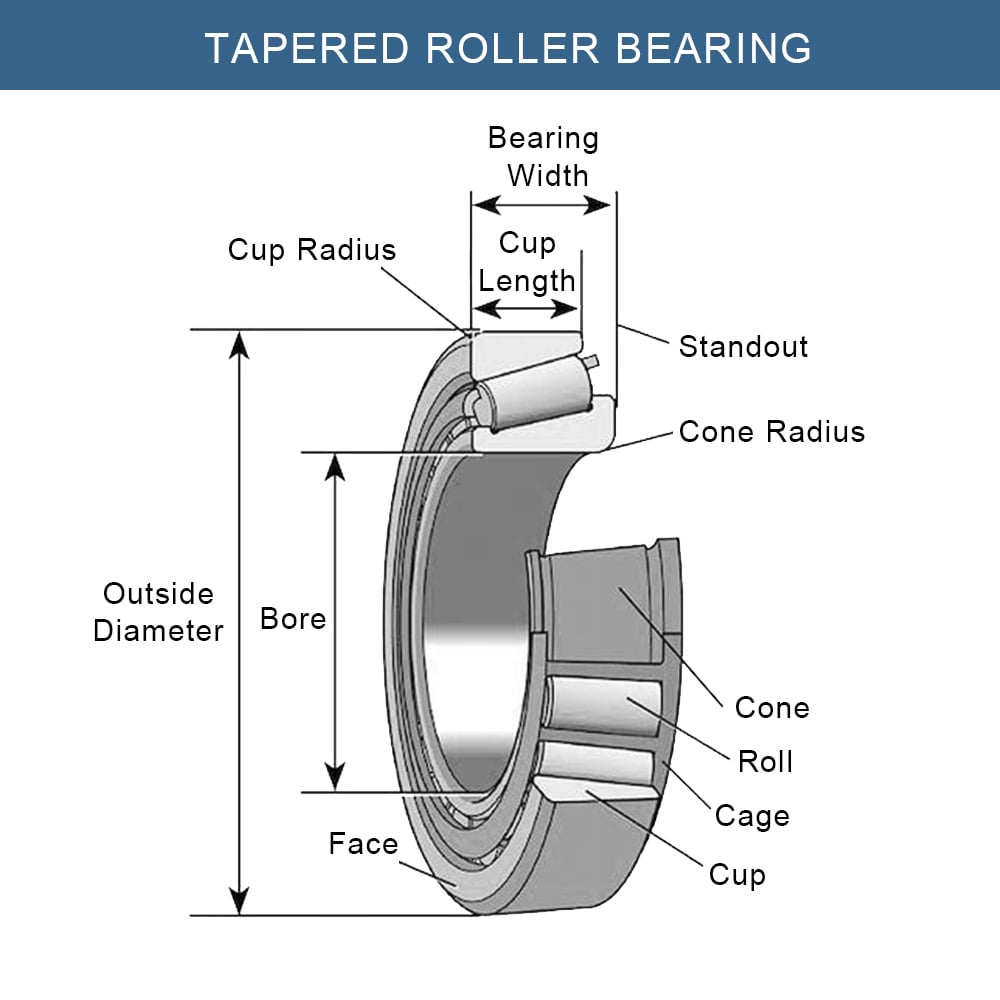
Advantages and Benefits
- High Load-Carrying Capacity: One of the standout features of tapered roller bearings is their ability to support heavy loads. This is due to the larger contact area provided by the tapered design.
- Precision and Accuracy in Operations: These bearings are known for their precision and accuracy, making them suitable for applications requiring meticulous control over bearing movements and loads.
- Handling Axial and Radial Loads: Tapered roller bearings are adept at handling both axial (thrust) and radial loads, a unique capability arising from their design. The arrangement of the tapered rollers allows them to effectively manage loads in multiple directions.
Common Applications
- Automotive Industry: Frequently used in car and truck wheel bearings.
- Heavy Machinery: Applied in construction and mining equipment.
- Agricultural Equipment: Used in various high-load agricultural machines.
- Industrial Gearboxes: Essential in gearboxes requiring precise load handling.
Limitations in Specific Use Cases
- Speed Limitations: Tapered roller bearings may not be suitable for high-speed applications due to their design.
- Misalignment Sensitivity: They can be sensitive to misalignment issues, requiring careful installation and maintenance.
- Complexity in Mounting and Disassembly: Due to their internal design, mounting and disassembling these bearings can be more complex compared to other types.
In conclusion, tapered roller bearings are invaluable in applications requiring the handling of heavy loads with high precision. However, understanding their limitations is crucial to ensure they are employed in appropriate use cases, maximizing their efficiency and lifespan.
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings are characterized by their unique design, featuring two rows of barrel-shaped rollers oriented diagonally across the inner and outer raceways. This design allows for the bearing to adjust to varying degrees of alignment and load directions, making them highly versatile.
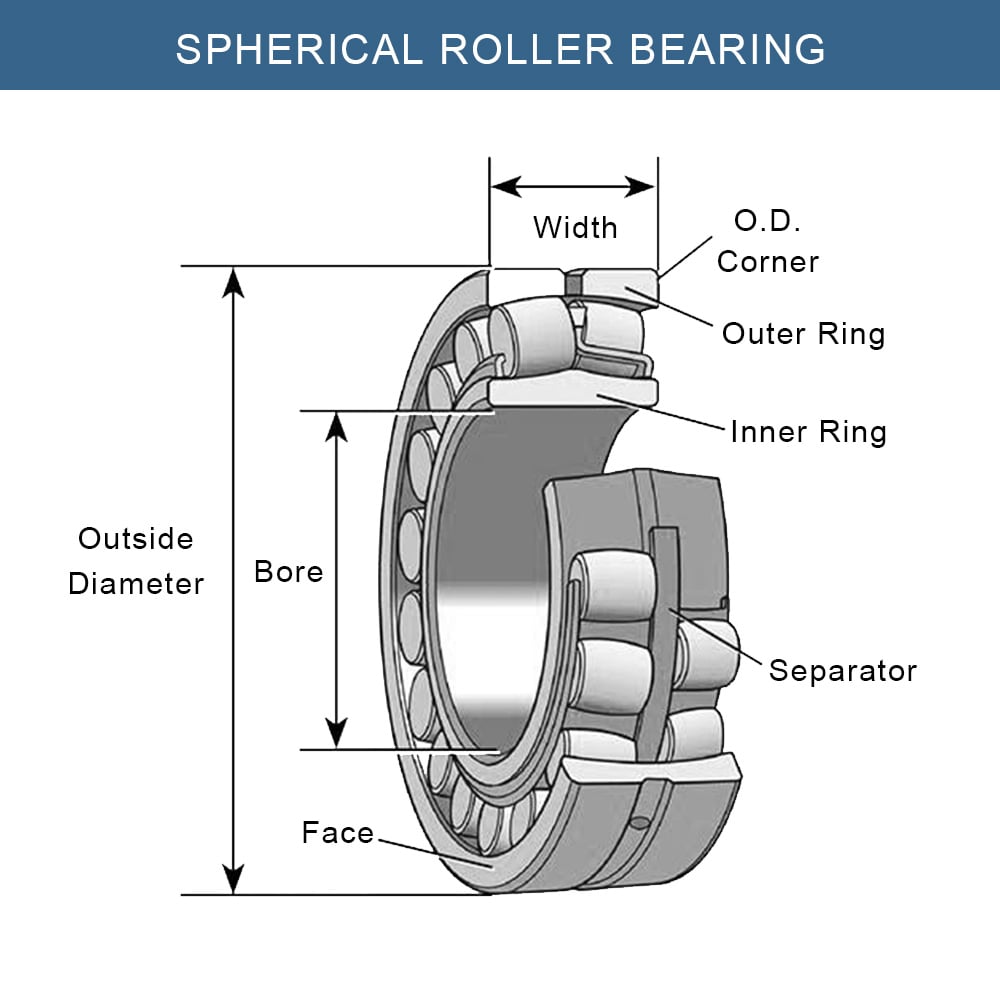
Key Advantages
- Self-Alignment Capability: A standout feature of spherical roller bearings is their ability to self-align. This is due to the curvature of the outer ring raceway, which aligns with the rotational axis.
- Exceptional Load Capacity: They are designed to handle high radial loads and moderate axial loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Misalignment Tolerance: Spherical roller bearings can tolerate misalignment to a certain degree, compensating for shaft deflection and alignment errors without compromising performance.
Typical Use Cases
- Heavy Machinery: Commonly used in sectors requiring heavy load support, such as mining and construction.
- Wind Turbines: Ideal for applications like wind turbines that experience varying loads and directions.
- Paper Mills: Their robustness makes them suitable for the demanding environment of paper mills.
- Gearboxes and Pulleys: Frequently used in large industrial gearboxes and pulley systems where misalignment may occur.
Limitations and Constraints
- Speed Limitations: While they can handle heavy loads, spherical roller bearings may not be the best choice for applications requiring very high-speed operations.
- Complexity and Cost: Their advanced design can make them more complex and costly compared to simpler bearing types.
- Size and Weight: Generally, spherical roller bearings are larger and heavier, which might be a constraint in applications with space or weight limitations.
In summary, spherical roller bearings offer unique advantages like self-alignment and high load capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty and misalignment-prone applications. However, their limitations in speed, complexity, and size need to be considered to ensure they are chosen for appropriate use cases.
Comparative Analysis: Tapered Roller Bearing vs. Spherical Roller Bearing
Understanding “Tapered Roller Bearing vs Spherical Roller Bearing” is crucial for selecting the right bearing for specific applications. Here, we compare these two types of bearings based on several key parameters.
Load Handling and Distribution
- Tapered Roller Bearings: They excel in handling combined loads (both radial and axial). The tapered design allows for effective distribution of loads across the bearing, making them ideal for heavy-load applications.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: These bearings are primarily designed for high radial loads with a moderate level of axial loads. Their barrel-shaped rollers make them more suitable for applications where loads come from varying directions.
Precision and Alignment
- Tapered Roller Bearings: Known for their precision, these bearings are suitable for applications requiring high accuracy. However, they are sensitive to misalignment and need precise installation.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: They offer self-aligning capabilities, making them more forgiving in applications with potential shaft misalignment. This feature reduces the risk of performance degradation due to alignment errors.
Suggested Applications
- Tapered Roller Bearings: Best suited for automotive wheel bearings, gearboxes, and other applications where heavy combined loads are present.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: Ideal for heavy machinery in mining and construction, wind turbines, and applications where misalignment might occur.
Maintenance Requirements
- Tapered Roller Bearings: Require careful monitoring and precise alignment during installation and maintenance to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: While they can handle misalignment, regular maintenance is still crucial to prevent premature wear due to heavy loads and environmental factors.
You can also refer to the following table.
|
Feature |
Tapered Roller Bearings |
Spherical Roller Bearings |
|
Load Handling |
Combined radial and axial loads |
High radial and moderate axial loads |
|
Precision & Alignment |
High precision, sensitive to misalignment |
Self-aligning, more tolerant to misalignment |
|
Typical Applications |
Automotive, gearboxes |
Heavy machinery, wind turbines |
|
Maintenance Needs |
Precise alignment and monitoring |
Regular maintenance, more forgiving to alignment errors |
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate bearing for any application hinges on a few critical factors:
- Load Type and Magnitude: Assess if the load is radial, axial, or combined. For heavy combined loads, tapered roller bearings are ideal, whereas spherical roller bearings are better for high radial loads with some axial load.
- Speed and Temperature Requirements: Consider the operational speed and temperature range. Bearings must be capable of handling the specific RPM and heat levels without degradation.
- Misalignment Requirements: Evaluate the potential for misalignment. Spherical roller bearings are preferable in applications where misalignment is likely.
Practical Examples
- In heavy industrial applications with high radial loads and misalignment, spherical roller bearings are typically the best fit.
- For precision-demanding, high-speed applications with combined loads, tapered roller bearings are more suitable.
Conclusion
A summary of the key differences between tapered and spherical roller bearings is provided to aid in making an informed decision. It's emphasized that quality and expert consultation are crucial in the selection process. Lily-Bearing offers a range of bearing options tailored to diverse industrial needs.
Keep Learning