Ball Bearing Vs Wheel Bearing
Industrial bearings play an integral role in the operation of various machinery and vehicles, reducing friction and enhancing performance. This blog aims to dissect the differences between two common types: ball bearings and wheel bearings. By understanding these differences, one can make better decisions for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of machinery.
Understanding Ball Bearings
What Are Ball Bearings?
Ball bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing that utilizes balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races. Essentially, they consist of a series of hard steel balls that roll between two rings, known as the inner and outer races. This design minimizes friction and allows for smooth rotation of the assembly.
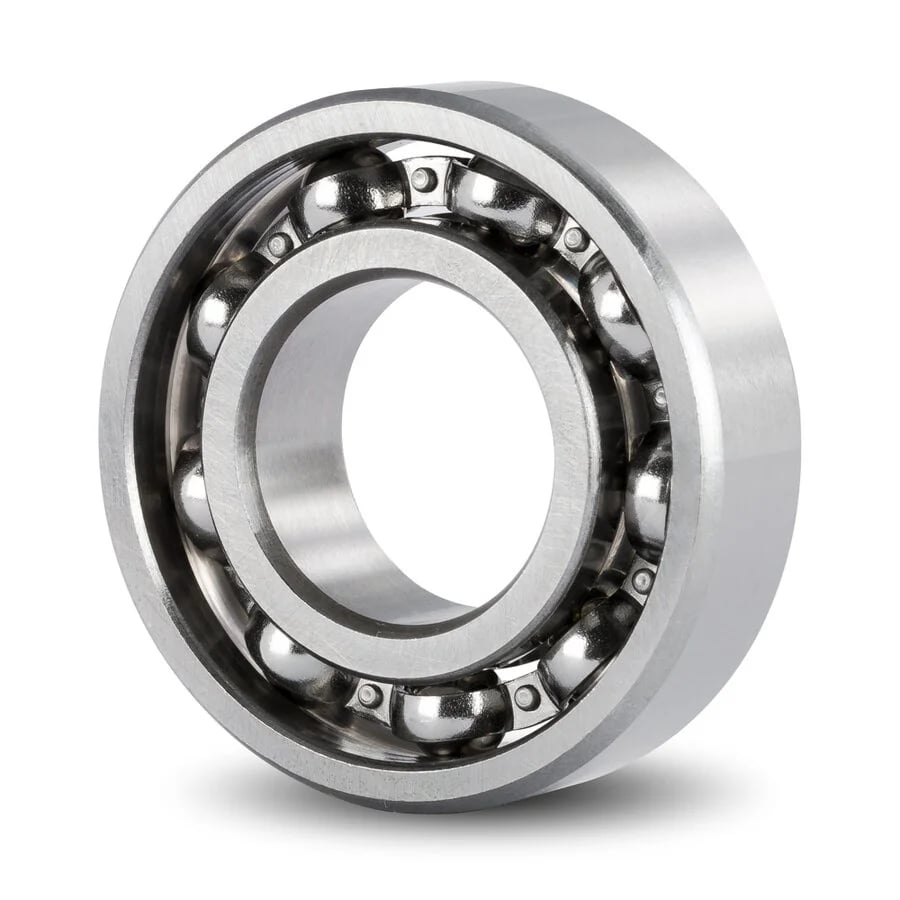

Fundamental Characteristics
- Design: Comprises an inner and an outer ring with a series of balls in between.
- Function: Primarily designed to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads.
- Mechanism: The balls in the bearing act as the rolling element, facilitating smooth motion with minimal resistance.
Common Applications in Industrial and Mechanical Systems
Ball bearings are widely used in a variety of settings, including:
- Precision Instruments: Such as in medical equipment, where high precision and low friction are crucial.
- Machinery: Used in everything from small motors to large industrial machinery.
- Automotive Industry: Integral in various automotive parts, including engines and gearboxes.
- Consumer Electronics: Essential in devices like hard drives and DVD players.
Advantages of Ball Bearings
- Efficiency: They offer highly efficient operation with reduced friction, leading to less wear and tear on machinery.
- Load Handling: Capable of handling both radial and axial loads effectively.
- Speed Capability: Ball bearings can operate at high speeds, making them suitable for applications like electric motors and automotive components.
- Versatility: Their simple design makes them adaptable to various applications across numerous industries.
Limitations of Ball Bearings
Despite their advantages, ball bearings have some limitations:
- Load Capacity: While they can handle both radial and axial loads, there is a limit to the weight they can support, making them unsuitable for extremely heavy applications.
- Sensitivity to Contaminants: Ball bearings can be sensitive to dirt and debris, which can affect their performance.
- Precision Requirements: They require precise alignment during installation, which can be challenging in some applications.
- Maintenance: To ensure longevity and optimal performance, regular maintenance such as lubrication is necessary.
Understanding Wheel Bearings
What Are Wheel Bearings?
Wheel bearings are a crucial component in vehicle wheel assemblies, connecting the wheel to the axle. Typically comprising an inner and outer ring, with steel balls or rollers in between, they facilitate the wheel's rotation on the axle with minimal friction. These bearings are engineered to support the vehicle's weight while absorbing radial and axial loads from various driving forces, including acceleration, braking, and cornering.
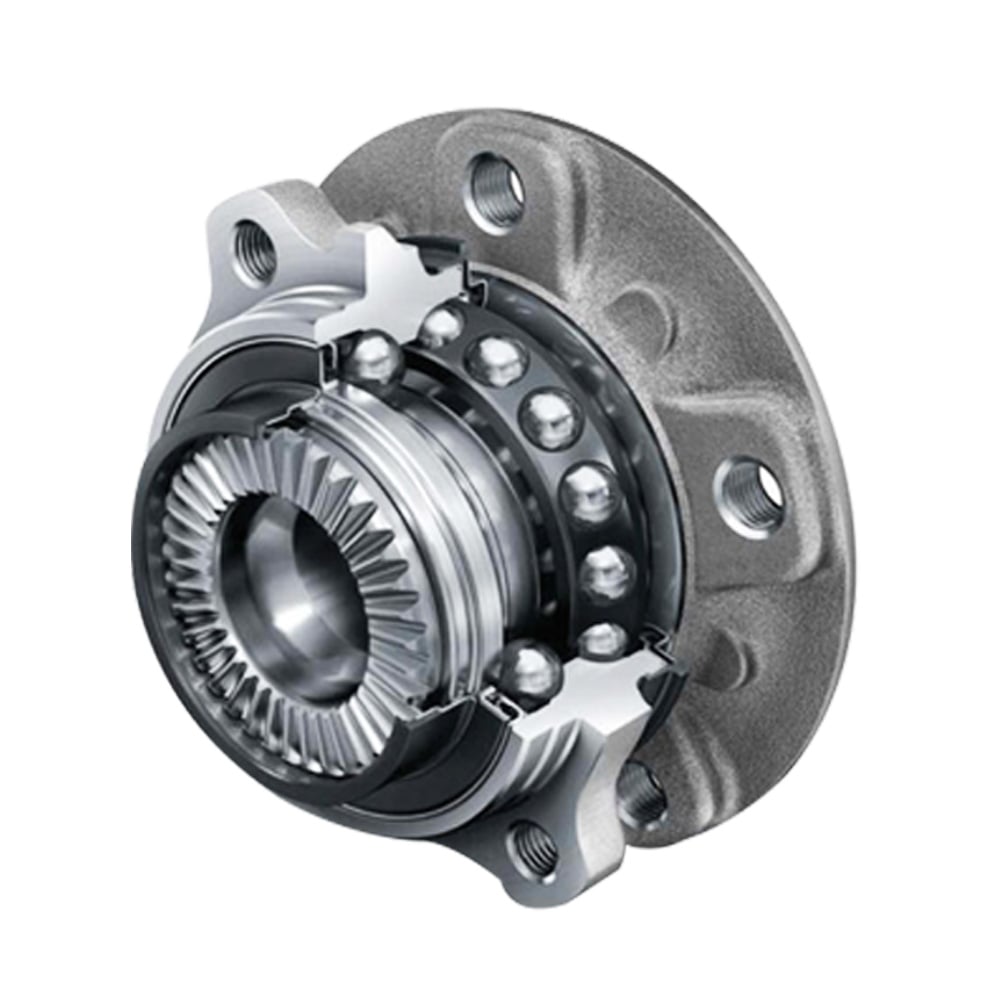

Specific Role in Automotive and Wheel Systems
- Load Support: Wheel bearings are designed to bear the entire weight of a vehicle, a crucial aspect for vehicle stability and safety.
- Friction Reduction: They reduce the friction between the moving parts of the wheel assembly, ensuring smooth wheel rotation.
- Enabling Movement: Wheel bearings allow for free wheel movement and play a critical role in the steering mechanism, contributing to responsive and controlled driving.
The Critical Function of Wheel Bearings
- Safety and Stability: They are integral to the vehicle's handling and stability, impacting overall driving performance and safety.
- Durability: Wheel bearings are built to withstand challenging road conditions and the constant pressure of vehicle weight and movement.
Advantages of Wheel Bearings
- Reliability: In the context of vehicles, wheel bearings are known for their robustness and ability to perform under the demanding conditions of road use.
- Performance: They contribute significantly to the overall handling and performance of a vehicle, enabling smooth and efficient wheel function.
- Longevity: Designed for durability, wheel bearings can last a long time when maintained properly, though their lifespan varies based on usage and conditions.
Challenges with Wheel Bearings
Despite their advantages, wheel bearings can face several challenges:
- Wear and Tear: Continuous exposure to road conditions, impacts, and heavy loads can lead to wear and tear.
- Contamination: They can be prone to damage from water, mud, and other contaminants, which can deteriorate the bearing's internal components.
- Maintenance and Replacement: While they are low maintenance, once wear sets in, wheel bearings require careful replacement. Incorrect installation or using improper tools can lead to premature failure.
- Symptom Recognition: Identifying issues with wheel bearings can be challenging, as symptoms like noise or irregular tire wear might be attributed to other vehicle problems.
Ball Bearing vs Wheel Bearing: A Comparative Analysis
|
Aspect |
Ball Bearings |
Wheel Bearings |
|
Structure |
Inner and outer rings with steel balls in between. |
Inner and outer rings with steel balls or rollers. |
|
Design Purpose |
Minimize rotational friction; suitable for high-speed, precision applications. |
Support vehicle weight; enable smooth wheel rotation under load. |
|
Applications |
Used in machinery, electronics, and automotive components for high-speed operations. |
Primarily found in automotive wheel systems for vehicle stability and movement. |
|
Performance |
Efficient with reduced friction; ideal for high-speed applications. |
Robust, handling constant vehicle load and varying driving conditions. |
|
Maintenance |
Require precise alignment and lubrication. |
Generally lower maintenance but require regular checks. |
Selecting the Right Bearing for Your Needs
When deciding between ball and wheel bearings, consider:
- Load and Speed: Ball bearings are optimal for high-speed, moderate-load applications. Wheel bearings are suited for heavy loads, as in vehicles.
- Application Environment: Ball bearings may require more maintenance in harsh conditions, while wheel bearings are typically more robust.
- Precision vs. Durability: Use ball bearings for high precision; choose wheel bearings for durability under constant, heavy loads.
- Installation and Maintenance: Ball bearings need precise alignment and regular lubrication. Wheel bearings generally have simpler installation and lower maintenance.
- Cost: Consider both initial purchase and long-term maintenance costs.
Conclusion
In essence, ball bearings are optimal for high-speed, precision tasks, whereas wheel bearings are designed for durability under heavy loads in vehicles. Selecting the right bearing is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. At Lily-Bearing, we provide a variety of bearings to meet your specific needs, helping you make well-informed choices for your projects or vehicles.
Keep Learning