Sign in
New customer? Start here
Cancel
Industrial Bearings
What are Industrial Bearings?
Industrial bearings are essential components used in various industrial applications to provide movement, support loads, and reduce friction. These highest quality bearings are meticulously engineered to ensure precision, reliability, and durability, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of a wide array of machinery.
Characteristics of Industrial Bearings
- Load Handling: Able to handle radial, axial, or a combination of both types of loads.
- Reduced Friction: Designed to reduce rotational friction, aiding the smooth operation of industrial equipment.
- Durability: Robustness of industrial bearings allows them to withstand high-speed operations and severe environments.
- Material Diversity: Industrial bearings are crafted from various materials like stainless steel and ceramics, aligning with application needs.
Main Types of Industrial Bearings
Industrial bearings come in a variety of types, each with its own specific applications.
- Ball Bearings: Reduce rotational friction, ideal for high-speed applications.
- Roller Bearings: Excel in heavy-load situations due to line contact, offering higher load capacity.
- Slewing Ring Bearings: Handle axial, radial, and moment loads, crucial for heavy machinery like cranes.
- Cam Followers: Efficiently manage high radial loads, reducing friction in motion control tasks.
- Plain Bearings: Operate with sliding motion, ideal for high load-carrying needs.
- Linear Bearings: Provide low friction motion along a single axis, perfect for precision tasks like CNC machines.
Brands of Industrial Bearings
Numerous brands exist within the market of industrial bearings, such as:
- SKF: a Swedish manufacturer offering durable, high-performance, energy-efficient bearings.
- EZO: a Japanese manufacturer specializing in miniature and precision ball bearings, known for their compact and high-speed bearings.
- TIMKEN: U.S.-based brand known for robust bearings that excel in extreme load and condition handling.
- IKO: Specializes in needle bearings and linear motion guides, preferred for precision-oriented applications.
Advantages of LILY’s Industrial Bearings
Industrial bearings from LILY Bearing offer several advantages over their competitors, including:
Close
- Competitive Pricing
- Customization Flexibility
- Rapid Global Delivery
- Customer-Centric Approach

Accessories
Aerospace Bearings

Ball Bearings

Bearing Applications

Cam Followers
Ceramic Bearings

Custom Bearings

Guide Wheel

Mounted Bearings

Plain Bearings

Polyurethane Rollers

Roller Bearings
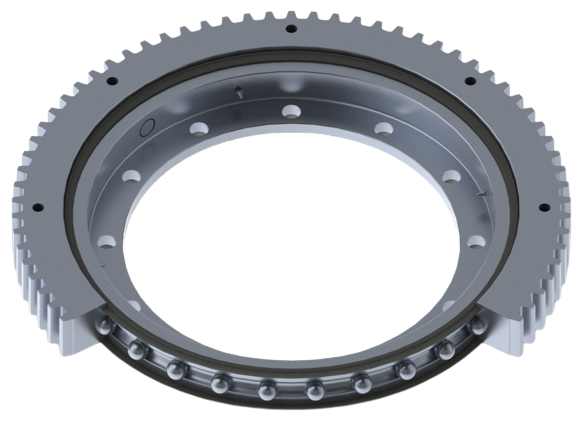

Slewing Ring Bearings

Stainless Steel Bearings
More Products:
Combined Bearings.
Linear Bearings.
Slewing Drivers.
Super Precision Bearings.
Wire Race Bearing.