How to Remove a Bearing: Methods and Tips
Removing a bearing from machinery is a critical task that can influence the longevity and performance of both the bearing and the equipment itself. Understanding how to remove a bearing with precision and care is paramount to ensure the machinery's integrity and the safety of the operator. This comprehensive guide will outline the key methods and tips for efficient bearing removal, ensuring you're equipped with the knowledge to perform this task effectively.
Bearing Removal Methods
Bearing removal refers to the process of detaching bearings from their operational position within machinery or equipment. The removal process involves carefully extracting these bearings without causing damage to either the bearings themselves or the shaft as well as the other surrounding components. This task requires specific tools and techniques, depending on the type of bearing, its location, and how it is mounted within the machinery.
Proper bearing removal is essential for safeguarding equipment from damage, ensuring the safety of maintenance personnel, and maintaining the integrity of the industrial bearings for potential reuse. Employing correct techniques not only prevents costly repairs and downtime but also enhances operational efficiency and ensures compliance with relevant safety and industrial standards. This approach is vital in minimizing risks and expenses while maximizing the longevity and performance of machinery.
Here, we provide a detailed look at various removal techniques and offers professional advice to tackle the task at hand.
Bearing Puller
The bearing puller is a specialized tool designed for the safe and efficient removal of bearings. This method is favorable for several reasons:
- Minimizes Machinery Damage: Bearing pullers are designed to extract bearings without applying pressure on adjacent machine parts, preserving the integrity of the machinery and the shaft. This careful approach ensures that the components remain unharmed, enabling repeated use of the bearing if conditions allow.
- Suitable for a Wide Range of Bearings: Pullers can be adjusted to fit various bearing sizes, making them versatile tools in the maintenance toolkit.
- Available in Mechanical and Hydraulic Options: Whether dealing with small or large bearings, there's a puller to fit the job—mechanical pullers for standard jobs and hydraulic versions for heavy-duty applications.
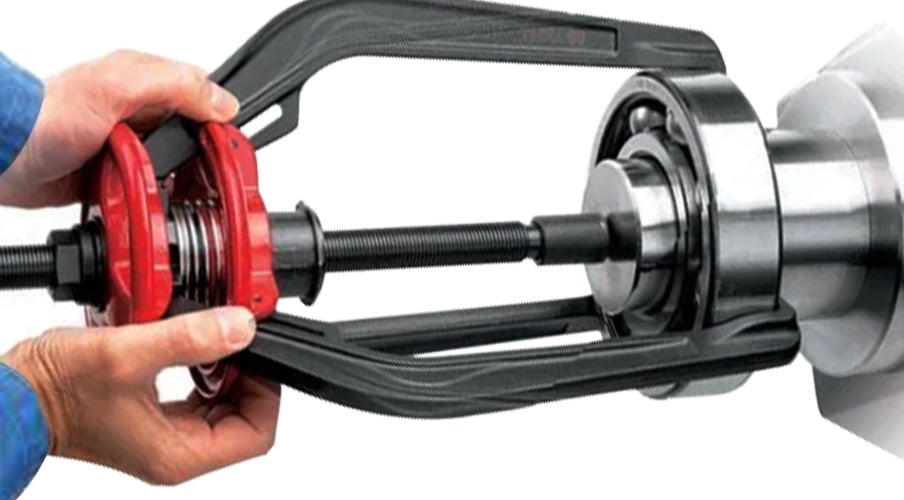

Hydraulic Methods
Hydraulic methods for bearing removal are a specialized technique employed in specific scenarios where conventional methods may not be feasible or effective. Understanding when and how to use these methods can be crucial for ensuring the safe, efficient, and damage-free removal of bearings, particularly in industrial settings.
When to Use Hydraulics for Bearing Removal:
Hydraulic tools are often the go-to solution in situations where bearings are tightly fitted or are part of large and heavy machinery. These situations typically include:
- Tight Interference Fits: Bearings that have a very tight fit (interference fit) on shafts or within housings can be challenging to remove without the right equipment. Hydraulic pullers can exert a controlled, yet powerful force, making them ideal for such applications.
- Heavy Machinery: In the context of heavy industrial equipment, such as in mining, construction, or large-scale manufacturing, bearings are often larger and heavier. Manual removal methods can be impractical or unsafe in these instances, thus hydraulics offer a suitable alternative.
- Space Constraints: Sometimes, the physical space around a bearing does not allow for the use of traditional mechanical pullers. Hydraulic systems, with their compact and versatile design, can often fit into these tighter spaces.
- Precision and Control: One of the primary advantages of using hydraulic methods is the level of precision and control they offer. Unlike brute force methods, hydraulics allow for a gradual application of force, which can be closely monitored and adjusted as needed. This precision is crucial for preventing damage to the bearing or the surrounding machinery. It ensures that the force is evenly distributed across the bearing, reducing the likelihood of warping or misalignment.
Hot Oil and Steam
The hot oil and steam method is a specialized technique for bearing removal, leveraging thermal expansion to ease the extraction process. It’s crucial to understand both the methodology and its associated risks for safe and effective use.
Understanding the Method:
- Operation Principle: This approach involves heating the bearing or its housing, using either hot oil or steam, to expand the metal and create clearance for easier removal.
- Controlled Heating: Even and monitored heating is essential to avoid distortion or uneven expansion of the bearing or surrounding material.
Risks and Dangers:
Burn Hazards: Both hot oil and steam pose significant burn risks, necessitating stringent safety measures and protective gear.
- Material Damage: Overheating can alter the metallurgical properties of the bearing or housing, potentially leading to failure or reduced integrity.
- Fire and Explosion Risks: Particularly with hot oil, there's a danger of fire or explosion if overheated, highlighting the need for careful temperature control.
- Environmental Concerns: These methods require a safe workspace with adequate ventilation, especially when using hot oil.
- Precision Issues: Uneven heating can result in warping, affecting the precision fit required for bearings.
Brute Force
The brute force method is the least recommended due to its potential to:
- Damages Equipment: Applying uneven force can cause misalignment and damage to machine parts.
- Increases the Risk of Personal Injury: The unpredictable nature of this method poses significant safety risks.
Top Tips for Bearing Removal
To ensure a safe and successful bearing removal process, consider the following tips:
- Follow Manufacturer's Instructions: Adherence to the guidelines provided by the manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the bearing remains in a reusable condition if that is the intended outcome.
- Seek Professional Training: Proper training can greatly reduce the risk of injury and machinery damage.
- Correct Tooling: Make sure puller jaws or hydraulic cylinders are the right size and shape for the specific bearing.
- Safety First: Whenever possible, avoid using high-risk methods such as hot oil or steam.
- Expert Consultation: When in doubt, consult with a maintenance product specialist to guide you through the process.
It is worth noting that in instances where the bearing cannot be disassembled due to design constraints, it underscores the importance of considering bearing removal at the initial design stage of a product. This foresight can greatly simplify maintenance procedures and extend the lifecycle of both the bearing and the machinery. It's a proactive measure that ensures ease of disassembly without damage to components.
In Summary
To conclude, this blog's insights on “how to remove a bearing” highlight the cruciality of choosing safe and effective removal methods. The right approach is key to protecting both the machinery and personnel. We advocate for careful selection of the appropriate removal technique tailored to each specific task. At Lily-Bearing, we underscore this with our commitment to providing high-quality bearings, ensuring dependable and durable performance in all applications. Trust Lily-Bearing for bearings that align with the industry's best practices in maintenance and removal.
Keep Learning