Shielded Vs Sealed Bearings
Bearings play a crucial role in numerous applications, reducing friction and enabling smooth, efficient operations. Among the wide range of bearing types, the choice between shielded and sealed bearings often arises, each offering unique attributes and benefits. This article delves into the nuances of shielded vs sealed bearings, shedding light on their distinct features, advantages, and appropriate use cases. Understanding these key differences can guide you to the optimal bearing choice for your specific application.
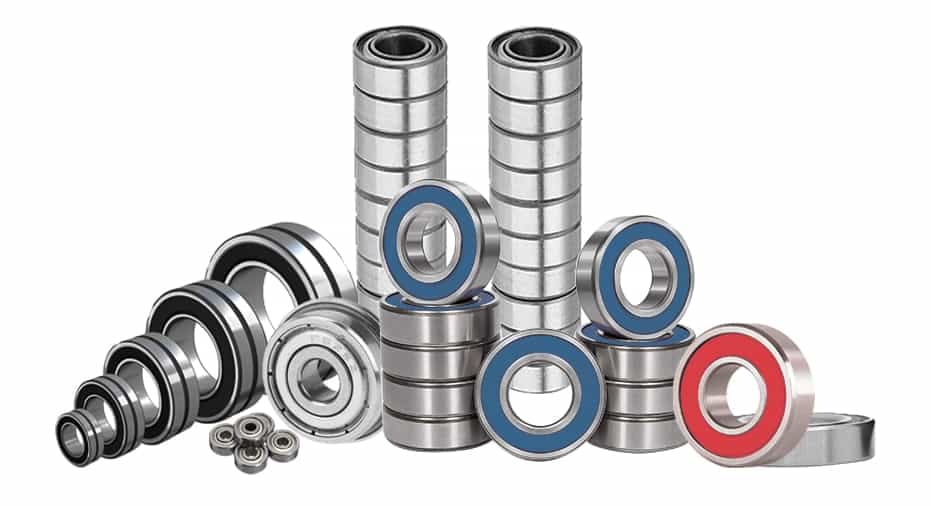

Understanding Shielded Bearings
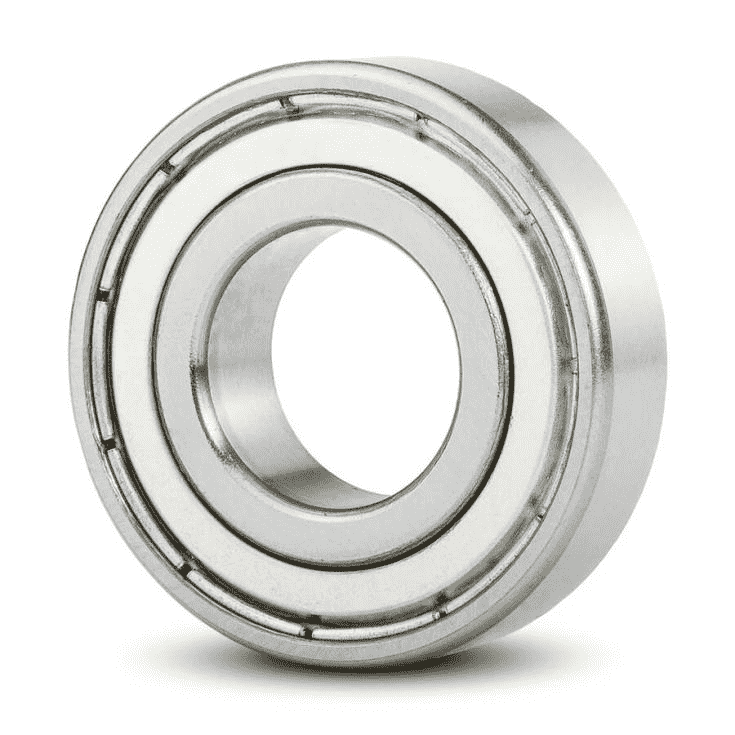
Shielded bearings incorporate a metal shield on one or both sides of the bearing to provide a physical barrier against larger foreign particles. The shield doesn't make direct contact with the inner race, creating a small gap. Therefore, the starting torque of the bearing is relatively small.
Shielded bearings include Shielded Bearings with the stamped metal cover and Shielded Bearings with Snap Ring (also known as also known as ZZNR bearings). Most bearings shielded Bearings belong to the former.

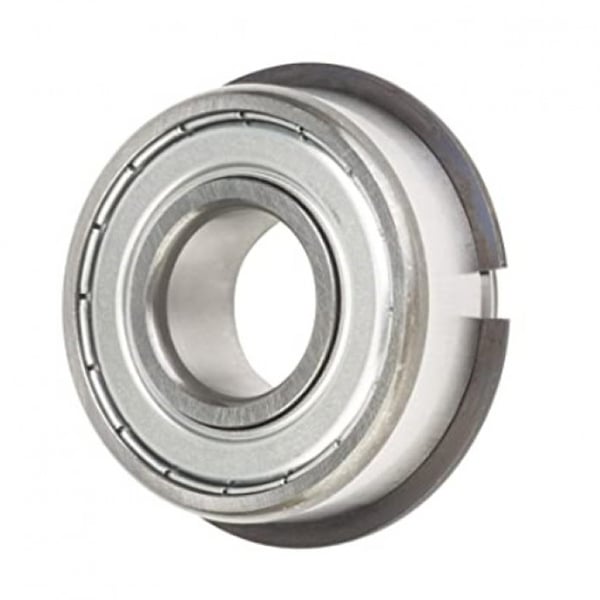
The latter allows for easy assembly and secure positioning within their housing due to the snap ring. This feature also prevents the bearing from moving axially, thereby enhancing its performance and lifespan. Particularly in the case of miniature bearings or thin section bearings, the snap ring provides a space-saving means of securing the bearing.

Advantages of Shielded Bearings
- Lower Running Torque: Since there's no frictional contact between the shield and the inner race, shielded bearings typically exhibit lower running torque.
- Cost-Effective: Shielded bearings are usually less expensive than their sealed counterparts while still providing a considerable amount of protection.
- High temperature resistance: Typically, Shielded Bearings can endure temperatures up to 250°, whereas standard Rubber Sealed Bearings have a heat tolerance limit of just 120° or at most 180°.
Limitations of Shielded Bearings
- Partial Protection: The shields offer limited protection and cannot fully prevent smaller particles or dust from entering the bearing.
- No Moisture Protection: The shields do not offer protection against the ingress of moisture or liquids, which could affect bearing performance.
- Limited Lifetime: The bearing's lifetime might be shorter than sealed bearings because contaminants and moisture can still infiltrate, albeit at a slower rate.
For this reason, shielded bearings are typically suitable for applications where the operating environment is relatively clean, and the primary concern is to keep the lubricant within the bearing while preventing larger particles from entering.
Exploring Sealed Bearings
Contrastingly, sealed bearings employ a non-metallic seal on either or both sides. These seals, typically made of rubber or synthetic materials, create a tight barrier that restricts the ingress of contaminants significantly more than their shielded counterparts. Sealed bearings can ensure a longer, more efficient, and trouble-free performance of mechanical systems and devices. They are widely used in precision industries like the food and beverage sector, or the medical industry, which prioritize cleanliness over the slight loss in efficiency.
LLB, LLU, LLH, LLE, and LLU-X are types of seals used in sealed bearings. These types of seal will impact the performance of bearings, including the level of protection, friction, and speed capabilities.
- LLB: These have non-contact seals with minimal friction, excellent for high-speed use. The synthetic rubber seal, molded to a steel plate, provides dust protection but has poor water resistance. They function effectively from -25℃ to 120℃.
- LLU: These have contact seals, offering robust dust and water protection. They exhibit medium torque, limiting their high-speed use, and operate effectively between -25℃ and 110℃. Ideal for highly contaminated areas, they are suitable where bearing replacement is challenging.
- LLH: LLH sealed bearings, featuring a light-contact synthetic rubber seal and an air hole design, strike a balance between speed and protection. They have a special lip to prevent foreign matter intrusion, providing excellent dust protection and good water resistance. With low torque, they exceed LLU-types in high-speed performance and operate efficiently between -25℃ to 120℃.
- LLE: LLE sealed bearings have a unique rubber seal that is highly water-resistant. Their standout feature is a three-lip contact, which boosts protection. This makes them suitable for areas with possible water or fluid contact.
- LLU-X: LLUX sealed bearings have contact seals made of synthetic rubber, providing strong dust and water resistance. They have medium torque, operate from -25℃ to 110℃, and are best for areas with high contamination or where bearing replacement is difficult.
Advantages of Sealed Bearings
- Enhanced Protection: Sealed bearings offer excellent protection against contaminants, such as dust, dirt, and moisture, enhancing the lifespan of the bearing.
- Lubrication Retention: The seal helps to retain lubricant inside the bearing, reducing the need for frequent re-lubrication.
- Reduced Maintenance: The seal minimizes the need for cleaning and maintenance, saving time and costs.
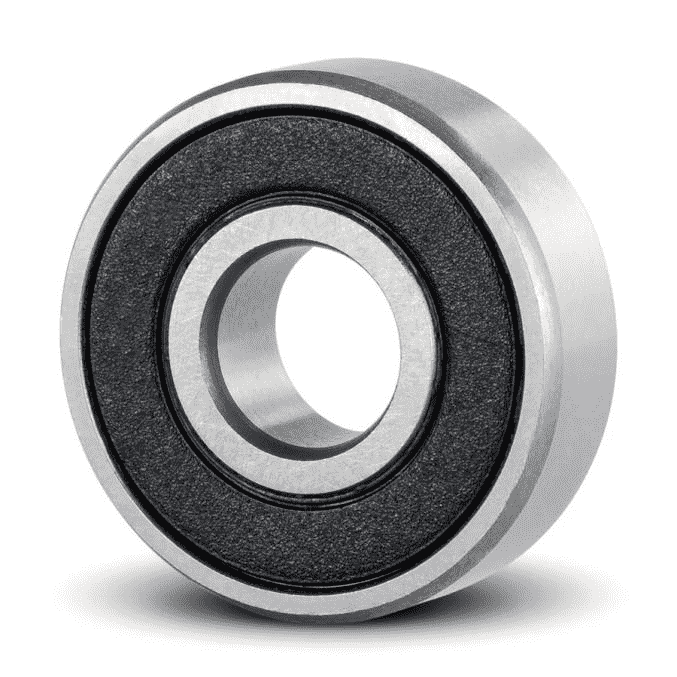
Limitations of Sealed Bearings
- Limited Speed: The friction from the seal can limit the maximum rotational speed of the bearing.
- Heat Generation: At high speeds, the seal can generate additional heat, which may affect bearing performance.
Shielded Bearings vs Sealed Bearings: Key Differences
Assessing key contrasts between shielded vs sealed bearings aids in effective application-based selection. Here's a succinct summary:
- Design and Construction: Shielded bearings use metal shields creating a gap, while sealed bearings have tight-contacting rubber or synthetic seals.
- Sealing Effectiveness and Contamination Resistance: Shielded bearings block larger particles. In contrast, sealed bearings offer superior protection against both large and small contaminants.
- Performance and Lifespan: Shielded bearings allow higher speeds but may have a shorter lifespan in contaminated environments. Sealed bearings operate at slightly reduced speeds due to seal friction but may outlast shielded bearings in high particulate environments.
Overall, the choice depends on the balance between speed, lifespan, maintenance, and contamination levels.
Factors to Consider in Choosing Between Shielded and Sealed Bearings
For bearing choice, consider contamination level and maintenance ease. Shielded bearings are best in clean, maintainable environments, while sealed bearings thrive in dirtier, hard-to-service areas. Industry standards may also guide the selection.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of shielded vs sealed bearings helps make informed decisions that cater to your specific needs. At LILY Bearing, we provide both options, allowing you to choose the one that best aligns with your application's requirements. We invite you to explore our comprehensive range, designed to cater to your bearing needs with utmost precision and quality.
Keep Learning