Types of Bearings Used in Machine Tool Spindles and Their Significance
In the world of machining, the words CNCs and high precision go hand in hand. The super-high tolerances today's complex parts have to meet come down to the precision of these machines. Even the slightest errors can lead to costly mistakes and drastically bring down the levels of productivity.
When it comes to efficiency of CNC machines, machine tool spindles are the most critical comments as they are primarily responsible for driving the cutting heads of a CNC. Since precision is important, even the slightest of vibrations can lead to disastrous outcomes. This is where the insights and knowledge of selecting the right ball bearing for the task at hand become crucial.

In this article, we dive deeper into the different types of ball bearing available on the market for use in machine tool spindles and understand the differences, thus allowing you to achieve optimal performance and reliability in your machining journey.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Type of Bearing
When it comes to machining, ball bearings are subjected to several factors that can affect their performance and, ultimately, the performance of the spindle. Every machining job is unique, but the physics of it is constant. A clear understanding of these factors will help you make better decisions that can take your machining skills to new heights.
- Speed: High spindle speeds mean increased friction, resulting in higher operating temperatures, which can damage learning if they are not designed for it. The type of bearing used in the spindle should be designed to handle these factors.
- Load: Bearings must be able to handle both radial and axial loads, which can vary depending on the application. Using a bearing in a situation it's not designed to deal with will lead to premature wear and tear, drastically reducing precision levels.
- Vibration: Vibrations can cause excessive wear and tear on bearings. Use bearings that are designed to dampen vibrations and maintain their accuracy and stiffness under these operating conditions.
- Contamination: No matter how good your dust extraction system is, dust and debris are inevitable during machining. This is another factor to consider, as it is best to use adequately sealed bearings to prevent contamination and maintain their performance.With these concepts clear, let's look at the various bearings used in machine tool spindles.
Types of Bearings Used in Machine Tool Spindles
There are four main types of ball bearings used in machine tool spindles, each with its own strengths and weaknesses that must be understood so that you can choose the best one for the task at hand.
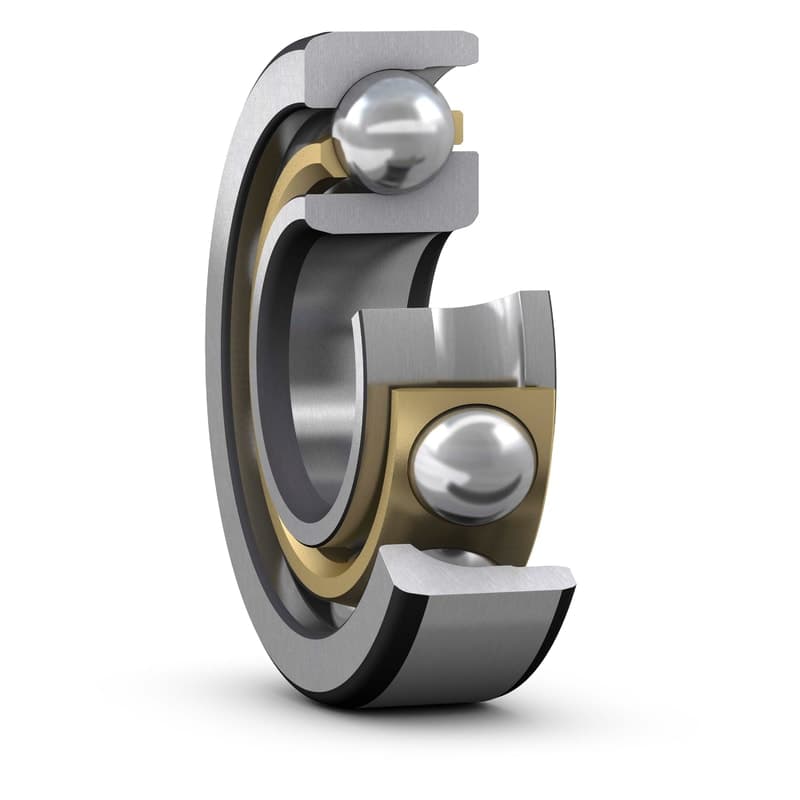 Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are designed to handle radial and axial loads in both directions simultaneously. They have a contact angle between the balls and the inner and outer raceways, allowing them to support axial loads in one direction while carrying radial loads. As a result, they are widely used in high-speed and precision applications where accuracy and stiffness are critical, such as machine tool spindles. Angular contact ball bearings are available in a range of sizes, materials, and configurations to suit specific applications.
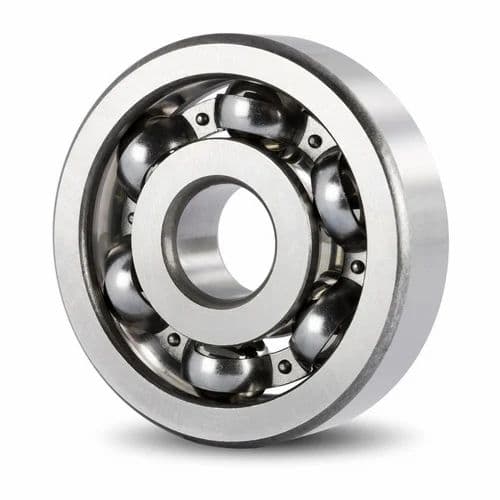 Radial or Deep Groove Bearings
Radial or Deep Groove Bearings
Radial or deep-groove ball bearings are the most commonly used type of machine tool spindles. They are designed to primarily handle radial loads and have a deep groove in their raceway, which allows the balls to roll smoothly over the raceway. These bearings are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations, making them suitable for a variety of applications. In addition, they are highly versatile and can operate at high speeds with low noise and vibration.
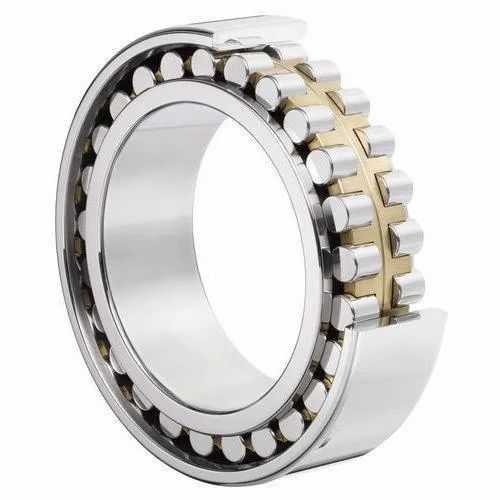 Roller Bearings
Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are another type of ball bearings used in machine tool spindles. They are similar to radial or deep-groove bearings but have cylindrical rollers instead of balls. The rollers in roller bearings allow them to handle heavier radial loads than radial bearings. They are also more tolerant of misalignment and can operate at higher speeds than radial bearings. As a result, roller bearings are commonly used in applications that require high radial load capacity and rigidity.
 Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust ball bearings are only designed to handle axial loads and are used in applications where heavy axial loads need support. They consist of two bearing discs and balls arranged in a cage. The balls are designed to support the axial load, while the washers are used to locate the bearing axially. Thrust ball bearings are suitable for high-speed applications and are commonly used in machine tool spindles that require high axial load capacity.
To make things easier, here is a table that compares the four bearings mentioned above to help you make better machining decisions.
| Type of Bearing | Load Capacity | Speed Rating | Load Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Contact Ball Bearings | High radial and axial load capacity | High-speed capability | Type of Loads Handled |
| Radial or Deep Groove Bearings | Moderate radial load capacity | Moderate to high-speed capability | Radial loads |
| Roller Bearings | High radial and axial load capacity | Moderate to high-speed capability | Radial and axial loads |
| Thrust Ball Bearings | High axial load capacity | Low to moderate speed capability | Axial loads |
To Sum Up
Machine spindles play a critical role in CNC machining, and selecting the appropriate ball bearing type is just as essential - each has its unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. If you are a CNC machinist or an enthusiast, this blog would help you make an informed decision about the type of ball bearing for your specific application.
Keep Learning