Cancel
CEZR 6311

| Part Number | CEZR 6311 |
| System of Measurement | Metric |
| Bearing Type | Ball |
| For Load Direction | Radial |
| Construction | Single Row |
| Seal Type | Open |
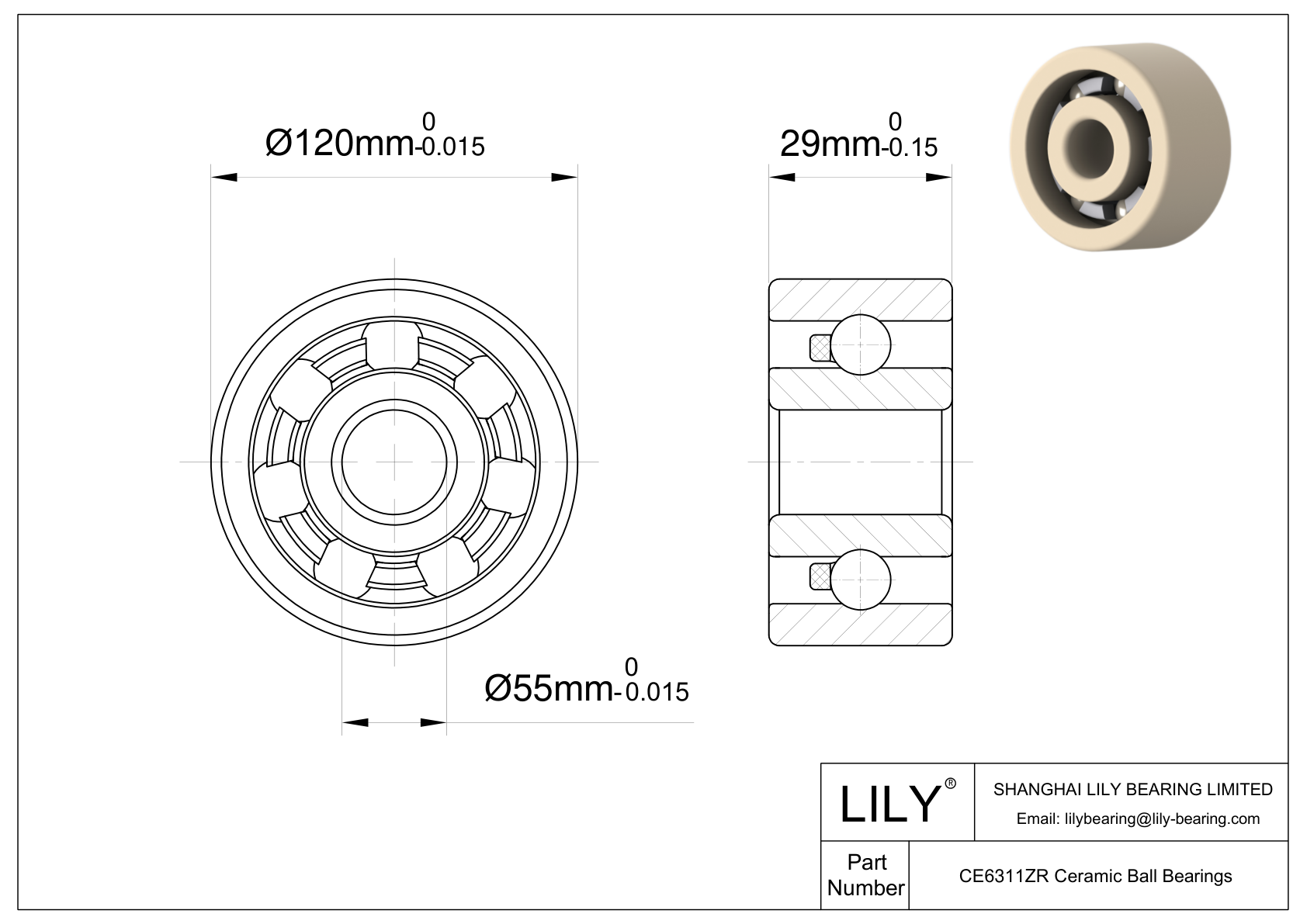
| Bore Dia | 55 mm |
| Bore Dia Tolerance | -0.015mm to 0 |
| Outer Dia | 120 mm |
| Outer Dia Tolerance | -0.015mm to 0 |
| Width | 29 mm |
| Width Tolerance | -0.150mm to 0 |
| Ring Material | Zirconia |
| Balls Material | Zro2 |
| Cage Material | PEEK |
| Dynamic Radial Load | 4833 lbf |
| Static Radial Load | 3038 lbf |
| Max Speed (X1000 rpm) | 3.92 |
| Lubrication | Without |
| Shaft Mount Type | Press Fit |
| ABEC Rating | ABEC-1 |
| Radial Clearance Trade No | C0 |
| Radial Clearance | 0.008mm to 0.028mm |
| Ball Dia | 20.638mm |
| Ball Qty | 8 |
| Temperature Range | -176 to 752 °F |
| RoHS | Compliant |
| Weight | 1012.50 g |
Design Features of CEZR 6311 Bearing
CEZR 6311 Bearing is a ball bearing that utilizes balls made from zirconia (zirconium dioxide - ZrO₂) ceramic as the rolling element. CEZR 6311 bore dia is 55 mm. Its out dia is 120 mm. CEZR 6311 width is 29 mm. Its ability to operate under high-speed conditions, coupled with its resistance to various challenging environments, makes it the go-to choice for professionals seeking both durability and precision. This bearing stands outs as a quintessential blend of precision engineering and material science.
What Benefits Can CEZR 6311 Bearing Provide?
- Low Friction: It inherently has a lower coefficient of friction compared to traditional steel ball bearings.
- Wear Resistance: Zirconia's hardness gives this bearing superior wear resistance, prolonging its service life.
- Non-Conductive: CEZR 6311 bearing is electrically non-conductive, making it suitable for applications where electrical insulation is crucial.
- Thermal Stability: Zirconia ceramic retains its properties over a wide range of temperatures and showcases excellent thermal stability.
- Corrosion Resistance: The ceramic material is resistant to various corrosive agents, making this bearing ideal for hostile environments.
What Can CEZR 6311 Bearing Be Used for?
CEZR 6311 Bearing excels in unique applications due to its specific properties:
- High-Temperature Environments: such as furnace conveyor systems or aerospace applications.
- Corrosive Settings: such as equipment in chemical processing plants or marine applications.
- Electrical Insulation: such as Electric motors or generators.
- Cleanroom Operations: such as Semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceutical production units.
- High-Speed Tools and Devices: such as dental drills or precision spindles operating at elevated RPMs.
Recommended Products