Cancel
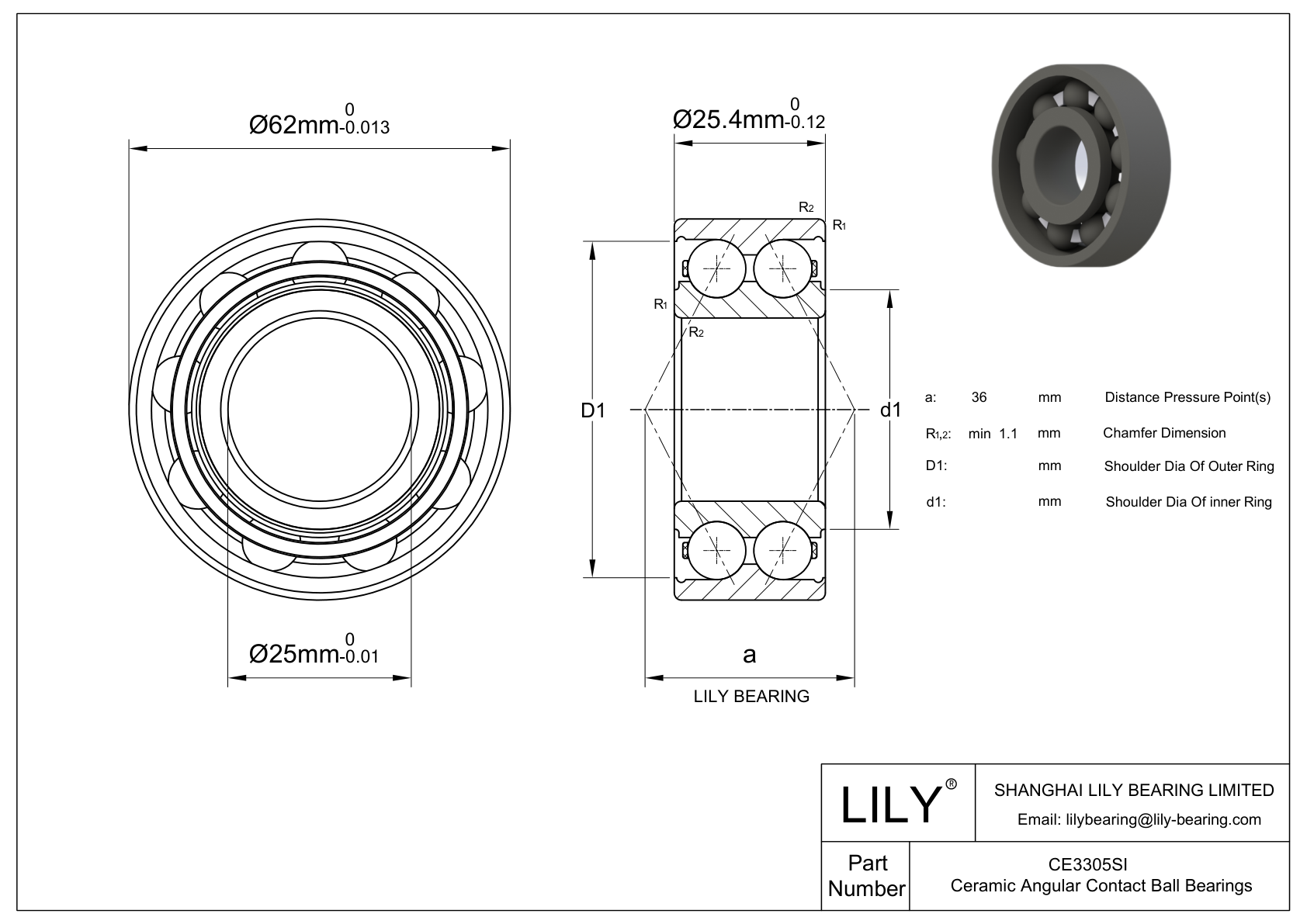
CE3305SI
| Part Number | CE3305SI |
| System of Measurement | Metric |
| Bearing Type | Ball |
| For Load Direction | Angular Contact |
| Construction | Double Row |
| Seal Type | Open |
| Bore Dia | 25 mm |
| Bore Dia Tolerance | -0.01 mm to 0 |
| Outer Dia | 62 mm |
| Outer Dia Tolerance | -0.013 mm to 0 |
| Width | 25.4 mm |
| Width Tolerance | -0.12 mm to 0 |
| Chamfer Dimension (r1 2)(min) | 1.1 mm |
| Distance Pressure Point (a) | 36 mm |
| Ring Material | Silicon Nitride |
| Balls Material | Si3n4 |
| Cage Material | PEEK |
| Dynamic Radial Load | 1644 lbf |
| Static Radial Load | 1113 lbf |
| Max Speed (X1000 rpm) | 7.92 |
| Lubrication | Dry |
| Temperature Range | -176 to 1472 °F |
| ABEC Rating | ABEC-1 |
| ROHS | Compliant |
| REACH | Compliant |
| Weight | 0.14 kg |
Design Features of CE3305SI Bearing
CE3305SI Bearing is characterized by its double-row angular contact configuration and the use of silicon nitride (Si3N4) ceramic balls. Its bore dia is 25 mm. Its out dia is 62 mm. Its width is 25.4 mm. CE3305SI Bearing is a sophisticated type of bearing designed to meet the needs of applications requiring high precision, durability, and load capacity.
What Benefits Can CE3305SI Bearing Provide?
- Increased Load Capacity: The double-row design enables higher axial and radial load handling, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- High-Speed Operation: Silicon nitride's low density reduces friction, allowing for efficient high-speed performance with minimal heat generation.
- Durability: Exceptional wear resistance of silicon nitride extends the bearing's life, especially in harsh conditions.
- Thermal Stability: This bearing remains stable across a wide temperature range, ensuring consistent performance in varied environments.
- Corrosion Resistance: Silicon nitride is highly resistant to corrosion, enhancing the bearing's longevity in aggressive settings.
- Electrical Insulation: The non-conductive nature of silicon nitride provides electrical insulation, protecting against electrical damage.
What Can CE3305SI Bearing Be Used for?
CE3305SI Bearing is suitable for applications such as:
- Industrial Machinery: In applications where both load capacity and precision are key, such as in manufacturing equipment.
- Aerospace and Defense: For components that require reliability under high loads and in extreme conditions.
- Automotive Engineering: In high-performance vehicles where robustness and speed are vital.
- Advanced Technology Equipment: In semiconductor manufacturing and robotics where precision and durability are crucial.


})
