Bearing Retainers & Cages
Bearing retainers, also known as cages, play a vital role in the efficient functioning of a bearing. They act as the backbone of the bearing system by maintaining the positioning of balls and rollers and ensuring load distribution. This blog post will walk you through the bearing retainers, their types, benefits, issues, and how to make an informed choice when selecting one.
What are Bearing Retainers?
Bearing retainers are designed to ensure the proper alignment and spacing of balls or rollers within a bearing, thus preventing them from rubbing against each other and allowing them to operate smoothly. They can also be used to facilitate lubrication by functioning as an oil reservoir, or by generating a solid film through the cage material or a coating applied to the cage.
Types of Bearing Retainers

Bearing retainers can be made from a variety of materials, depending on the specific application and requirements of the bearing.

Metal retainers: These are usually made of steel or bronze and are known for their durability and strength. They perform well under high loads and temperatures but can be susceptible to corrosion.
Carbon steel: for chrome bearings; AISI304 or AISI420 grade stainless steel; Preferred for higher-temperature applications; Brass: offering a high temperature up to 250 °C(480 °F); Bronze: Thin cross section, higher ball groove shoulders; high speed/ strength capability Crown type - inner ring guided; Ribbon type - mainly ball guided; Good for low to medium speeds
Plastic retainers: These are made of different types of plastics such as nylon, acetal, or PEEK. They are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for high-speed applications but may not be ideal for high-temperature environments.
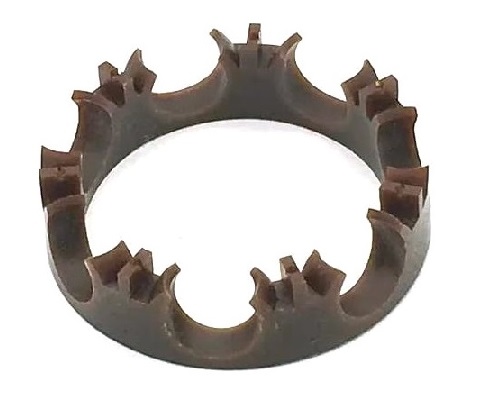
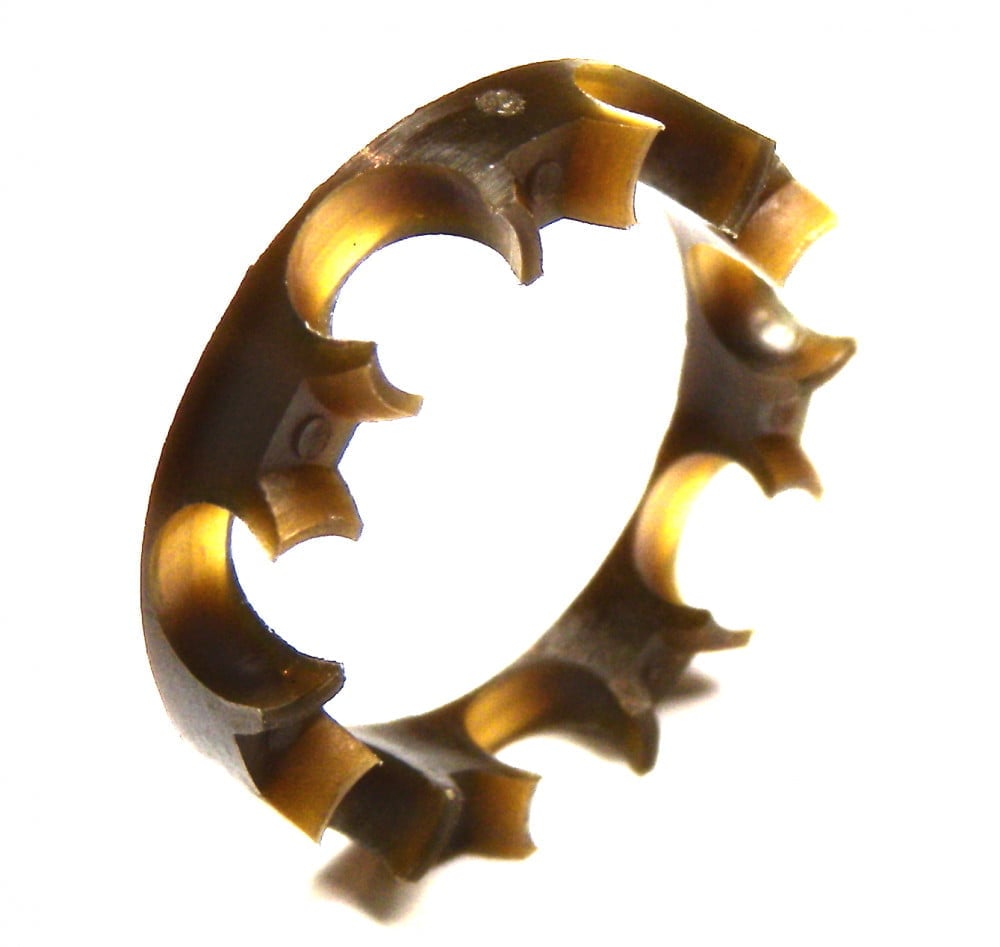
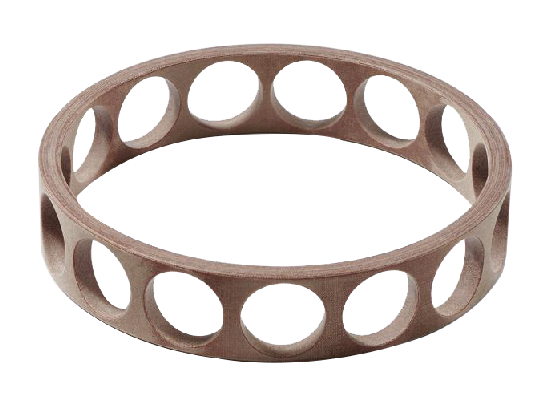







From the shape, common bearing retainers include:
- Crowned Retainers: These have a crown-like shape and are designed to reduce friction and wear between the balls and the retainer and are often used in ball bearings.
- Ribbon retainers: These are made of thin metal ribbons, offering a low-profile and lightweight solution for small bearings.
- Cage Retainers: Known as ball bearing cages, these common retainers have pockets to hold the balls in place, made of metal or plastic.
Benefits of Bearing Retainers
- Reduced Friction: Bearing retainers help to reduce friction between rolling elements and the raceways. This helps to improve the efficiency and speed of the bearing.
- Longer Bearing Life: Bearing retainers distribute the load evenly, reducing wear and tear, thereby increasing bearing lifespan.
- Improved Reliability: Bearing retainers prevent ball collision, reducing damage and premature bearing failure.
- Increased Load Capacity: Bearing retainers ensure even ball spacing, allowing the bearing to handle higher loads.
- Reduced Noise and Vibration: By keeping the balls in place, they reduce noise and vibration, critical in sensitive applications.
- Easy Maintenance:Bearing retainers are easy to replace, simplifying bearing maintenance.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Bearing Retainer
When selecting a bearing retainer, several factors come into play, significantly impacting the bearing's overall performance and longevity.
- Material and Type: Different materials, such as steel, plastic, or phenolic, offer varying levels of strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. Similarly, the type of retainer, be it a crown, ribbon, or cage, can influence factors like noise levels and speed capabilities.
- Load and Speed: These determine the required durability of bearing retainers High-speed or high-load applications necessitate robust and durable retainers capable of withstanding the associated stresses.
- Operating Environment: Factors like temperature and potential exposure to corrosive substances influence the choice of bearing retainers.
Common Issues with Bearing Retainers
- Wear and tear
- Contamination
- Misalignment
- Overloading
- Improper installation
- Fatigue failure
These problems can degrade bearing retainers and bearing performance over time. Remedying these concerns requires diligent inspection, replacement of damaged components, and adherence to regular maintenance procedures. Ensuring proper installation, alignment, and bearing load management, coupled with routine checks for fatigue signs, can mitigate these issues and prevent premature bearing failure.
Bearing Retainers vs. Ball Separators
Bearing retainers and ball separators both serve to maintain even spacing between the rolling elements in a bearing, reducing friction and wear. However, while retainers cater to a variety of bearing types, including both ball and roller bearings, ball separators are specifically designed for ball bearings. The choice between the two hinges on the bearing type and specific application requirements, with retainers offering broader versatility and separators excelling in high-speed ball bearing applications.
Conclusion
Bearing retainers are crucial for reducing friction and increasing the lifespan and reliability of bearings. Picking the right retainer is key to optimal performance. LILY Bearing provides a range of high-quality retainers, understanding their vital role in bearing efficiency. Remember, choosing the right retainer contributes to the overall success of your machinery. For expert guidance, LILY Bearing is always ready to help.
Keep Learning