Characteristics, Uses and Advantages of Stainless Steel Bearings
Compared with ordinary bearings, stainless steel bearings have stronger rust and corrosion resistance. They not only have obvious advantages in material, but also in terms of process and precision control, they are much stricter than ordinary bearings. During their working process, stainless steel bearings work steadily, with low noise, corrosion resistance and wide application. In this article, we will take a closer look at the characteristics, uses and advantages of stainless-steel bearings.
For information about Chrome Steel vs. Stainless Steel Bearings, please click here!
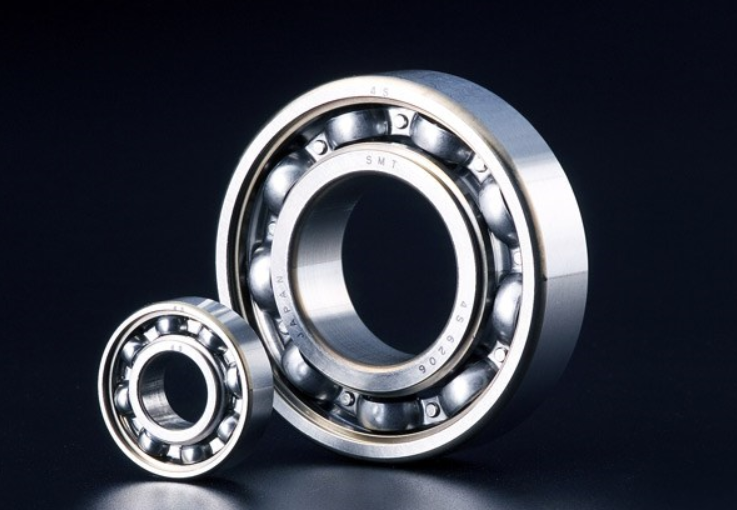

Classification and Characteristics of Stainless Steel Bearings
Stainless steel bearings, categorized by their steel composition and structural characteristics, come in various types to meet the demands of different applications:
Austenitic Stainless Steel Bearings
- Composition: Primarily chromium and nickel. Non-magnetic.
- Characteristics: Excellent corrosion resistance, good toughness, and moderate strength.
- Applications: Widely used in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and marine industries.
- Common Grades: 304 and 316, offering a balance of corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Martensitic Stainless Steel Bearings
- Composition: Higher carbon content with chromium. Magnetic.
- Characteristics: High strength and hardness, moderate corrosion resistance, heat-treatable for enhanced properties.
- Applications: Suitable for high-load, high-wear applications such as aerospace and industrial machinery.
- Common Grades: 440C is popular for its ability to achieve high hardness.
Ferritic Stainless Steel Bearings
- Composition: Chromium, low carbon content. Magnetic.
- Characteristics: Good corrosion and oxidation resistance, lower carbon content than martensitic, not heat-treatable.
- Applications: Used in environments where moderate corrosion resistance is sufficient.
- Examples: Bearings in appliances and automotive applications.
Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel Bearings
- Composition: A mix of chromium, nickel, and other elements. Can be magnetic or non-magnetic.
- Characteristics: Achieves high strength and corrosion resistance through heat treatment.
- Applications: Employed in aerospace and other high-stress applications.
- Examples: 17-4PH stainless steel is a common choice for its excellent strength.
Duplex Stainless Steel Bearings
- Composition: A mix of austenitic and ferritic structures.
- Characteristics: High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against stress corrosion cracking.
- Applications: Ideal for harsh environments like those in the oil and gas industry, and in marine applications.
- Examples: Grades like 2205 are used for their robustness in challenging conditions.
In most cases, AISI SUS440C stainless steel is used for bearing rings and rolling elements, which are vacuum quenched and tempered. The cage and seal ring frame materials are AISI304 stainless steel. If you choose a suitable lubricant, dust cover, etc., it can be used in an environment of -60℃~+300℃.
Based on the structure, stainless steel bearings can also be classified:
- Stainless steel ball bearings
- Stainless steel flanged ball bearings
- Stainless steel angular contact ball bearings
- Stainless steel thrust ball bearings
- Stainless steel needle roller bearings
- Stainless steel self aligning ball bearings
Advantages of Stainless Steel Bearings
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: stainless steel bearings are not easy to rust and have strong corrosion resistance.
- Ease of Cleaning: These bearings can be easily washed and do not require immediate re-lubrication to protect against rust.
- Liquid Compatibility: The materials used in these bearings allow for their operation within liquid mediums without impairing their performance or integrity.
- Reduced Lubrication Requirements: AISI 316 stainless steel bearings are inherently corrosion-resistant and don't always need oil or grease for protection, especially under low speed and load conditions where lubrication may not be necessary.
- Hygienic Properties: Stainless steel's natural resistance to corrosion contributes to its cleanliness, making it ideal for sanitary applications.
- Enhanced Heat Tolerance: Equipped with high-temperature polymer cages or non-full complement structures, stainless steel bearings can operate effectively in temperature ranges from 180°F to 1000°F, provided they are used with high-temperature grease.
Main Uses of Stainless Steel Bearings
Stainless steel bearings are widely used across various industries due to their corrosion resistance, durability, high mechanical strength and large load capacity. Key applications include:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Ideal for environments requiring strict hygiene standards, as they resist corrosion from frequent washdowns and exposure to food substances.
- Marine Applications: Used in shipbuilding and offshore equipment for their ability to withstand saltwater and harsh marine conditions.
- Medical Equipment: Essential in medical devices for their high cleanliness and resistance to sterilization processes.
- Chemical Processing: Suitable for chemical plants due to their resistance to corrosive substances and extreme environments.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Used in components exposed to challenging conditions, requiring high durability and reliability.
The Main Reason for Stainless Steel Bearing Fracture
The main reasons for the failure of stainless-steel bearings are defects and overload. When the external load exceeds the strength limit of the material and the part breaks, it is called overload fracture. The main cause of overload is the sudden failure of the host or improper installation. Defects such as microcracks, shrinkage cavities, bubbles, large foreign objects, overheated tissues, and local burns of bearing parts can also cause fracture at the defect when impact overload or severe vibration, which is called defect fracture. It should be pointed out that in the manufacturing process of the bearing, the re-inspection of raw materials, the quality control of forging and heat treatment, and the control of the processing process can correctly analyze the existence of the above-mentioned defects through the instrument, and the control must be strengthened in the future. But generally speaking, most of the fracture failures of stainless steel bearings that usually occur are overload failures.
Conclusion
We appreciate your time spent reading our article and trust that it offered insightful details on stainless steel bearings, including their types, benefits, applications, and fracture risks. For further information and a deeper exploration of these bearings, we invite you to visit Lily Bearing.
As a globally recognized bearing manufacturer, Lily Bearing provides a comprehensive range of top-quality stainless steel bearings and other bearing types at competitive prices, meeting a variety of industrial requirements. It is worth mentioning that our stainless steel bearings, particularly post-passivation, successfully endure a 168-hour salt spray test, showcasing their enhanced durability.
Keep Learning