The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Full Complement Bearings
Full complement bearings are often overlooked in the assembly of bearings. Unlike rubber seal, steel seal, open type, and UG bearings that we are familiar with, full complement bearings offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will delve into the benefits and limitations of full complement bearings.
What are Full Complement Bearings?
Full complement bearings are a type of rolling-element bearing that is designed to contain the maximum number of rolling elements, without using a cage or separator between them.
Common Types of Full Complement Bearings
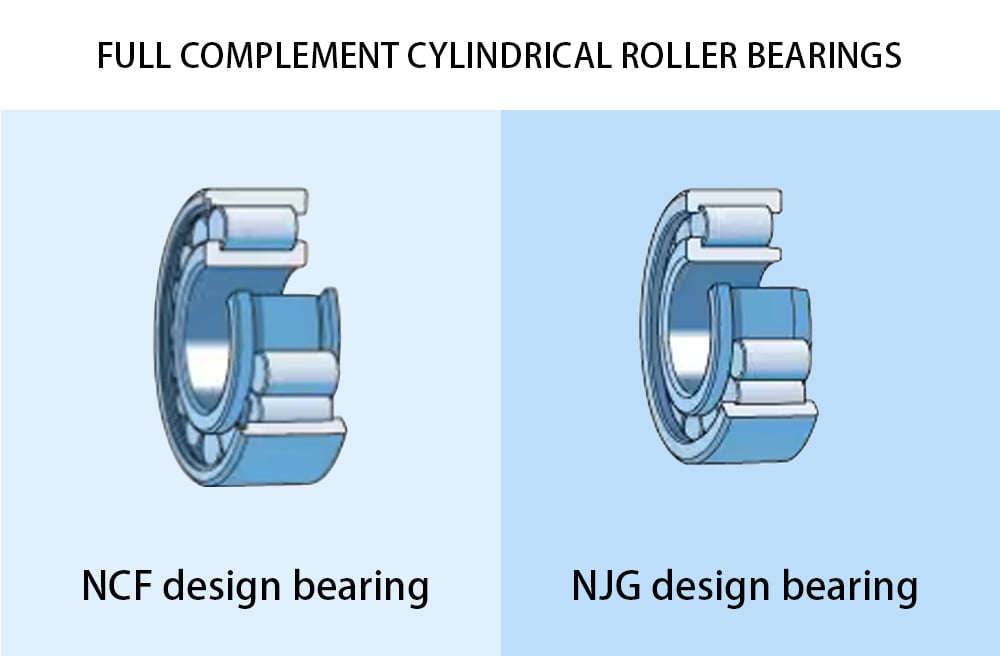
Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearings
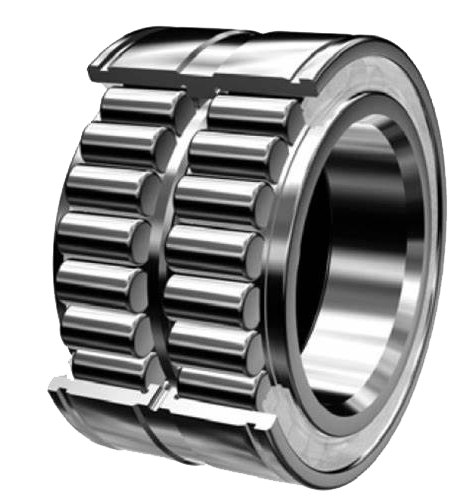

Double row full complement cylindrical roller bearing
- NCF design bearings: Feature two integral flanges on the inner ring and one on the outer ring, include a retaining ring in the outer ring opposite the integral flange for assembly cohesion, and are designed so that the retaining ring does not bear axial load during operation.
- NJG design bearings: Belong to the heavy 23 dimension series, designed for highly loaded, low-speed applications. These bearings feature two integral flanges on the outer ring and one on the inner ring, along with a self-retaining roller complement. This design allows the outer ring and roller complement to be separated from the inner ring easily, without the risk of rollers falling out, simplifying the process of mounting and dismounting.
- Matched bearings: Are precisely matched with a minimal cross-sectional height variance within a narrow tolerance range, essential for equal load distribution among bearings. Available as sets of two (designation suffix DR), three (designation suffix TR), or four bearings (designation suffix QR) to meet various application needs.
Full complement Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Full complement deep groove ball bearings are designed without a cage, allowing more balls to be included and thus providing a higher load capacity. This design makes them suitable for heavy-load applications where high speed is not a priority. However, their increased ball count results in higher friction, necessitating regular lubrication and maintenance.

Advantages of Full Complement Bearings
Full complement bearings offer several benefits over other types of bearings. Here are some of the advantages of using full complement bearings:
-
Increased Load Capacity
Full complement bearings are designed to have more rolling elements than standard bearings. As a result, they have a higher load capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. When compared to deep groove ball bearings, the dynamic load of a full complement ball bearing can be up to 45% higher, while the static load can be up to 45% higher as well.
For instance, The common deep groove ball bearing, 6203ZZ, has a dynamic load of 9550N and a static load of 4800N. With grease lubrication, it can handle speeds up to 171000rpm, and up to 201000rpm with oil lubrication. Alternatively, the crowded ball bearing, 6203 Full Complement Bearings, offers increased load capacity, with a dynamic load of 14000N and a static load of 7000N. While it is limited to 2000rpm with grease lubrication and 3000rpm with oil lubrication, it eliminates the problem of load capacity. In summary, Full Complement Bearings are a solution for handling heavy loads.
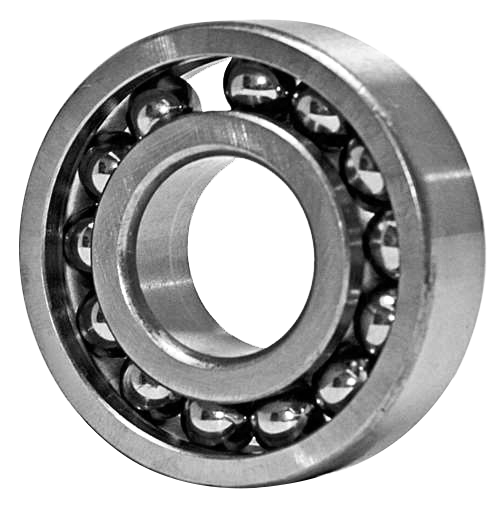

6203 Full Complement Bearing
-
Compact Design
They can achieve a higher radial load capacity within the same space, making them ideal for applications with limited radial space.
-
Increased Contact Area
The larger number of rolling elements increases the bearing's contact area, distributing the load more evenly and enhancing lifespan under heavy load conditions.
-
Cost-Effectiveness
The simpler design without a cage can be more cost-effective in terms of manufacturing.
-
Shock Resistance
They are better suited to absorb shock loads due to the increased number of rolling elements.
-
Low-Speed Applications
They are particularly effective in applications where high load capacity is required at lower speeds.
-
Better Durability
With more rolling elements in a full complement bearing, the load is distributed more evenly, resulting in better durability. This makes full complement bearings ideal for applications where high loads are present.
-
Improved Lubrication
Since full complement bearings have no cages or separators, there is more space for lubricant, which provides better lubrication. The lack of a cage also means that there is no friction between the cage and rolling elements, which reduces wear and tear.
Disadvantages of Full Complement Bearings
Although full complement bearings offer several advantages, they also come with some disadvantages. Here are some of the drawbacks of using full complement bearings:
-
Limited Speed
One of the major disadvantages of full complement bearings is that they have limited speed capabilities. Without a cage or separator to guide the rolling elements, they can become misaligned, leading to reduced speed and premature failure. Therefore, full complement bearings are not recommended for high-speed applications.
-
Increased Friction
With more rolling elements in a full complement bearing, there is increased friction between the elements. This can lead to increased heat and wear, reducing the overall lifespan of the bearing.
-
Dead Clamping
Full complement bearings have holes in the inner and outer rings that hold the rolling elements in place. At high speeds, the rolling elements can become stuck in these holes, leading to dead clamping and premature failure.
Conclusion
Full complement bearings offer several benefits, such as increased load capacity, better durability, and improved lubrication. However, they also have some disadvantages, such as limited speed capabilities, increased friction, and dead clamping. Therefore, full complement bearings are best suited for heavy-duty applications where speed is not a primary concern.
Keep Learning